Phytotherapeutic Alternatives to the Use of Finasteride and Dutasteride as 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Androgenetic Alopecia: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62742/2965-7911.2024.1.bjhh2Keywords:
Androgenetic alopecia, Phytotherapeutic medications, Side effects, Hair lossAbstract
Introduction: Androgenetic alopecia is the most common form of hair loss worldwide, occurring due to an excessive response to androgens. Its etiology is chronic and influenced by genetic and environmental factors, making it particularly challenging to treat. The primary treatment method currently involves the use of finasteride or dutasteride, which inhibit the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme. This enzyme is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), thereby hindering the progression of androgenetic alopecia. Alongside the widespread use of these treatments, concerns have emerged regarding potential side effects associated with this class of drugs. Notably, these include impairments in sexual function and possible psychological disorders, observed in some users. In this context, there has been growing interest in exploring alternative approaches to hair loss treatment using plant-based preparations and/or their active ingredients.
Material and Methods: The method employed for the preparation of this article was an integrative literature review to enable understandings of the use of phytotherapeutic herbs in people with hair loss.
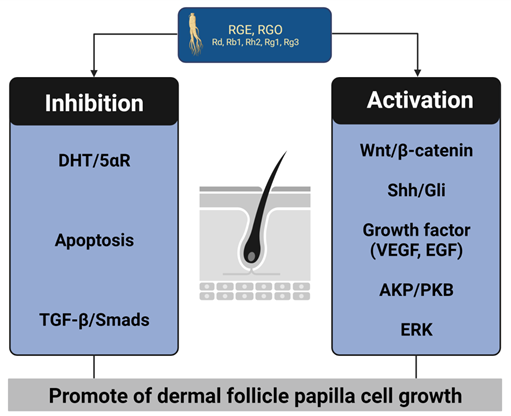
Results and Discussions: Several phytotherapeutic products are known to act against the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, inhibiting it and reducing hair loss without significant side effects. Plants like Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens), Ginseng (Panax ginseng), Green tea (Camellia sinensis), and Pumpkin seed oil (Cucurbita pepo) are notable for their antiandrogenic effects and have shown beneficial impacts in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. These could be considered viable options for treating androgenetic alopecia, serving as alternatives to finasteride and dutasteride.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Brazilian Journal of Hair Health

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




